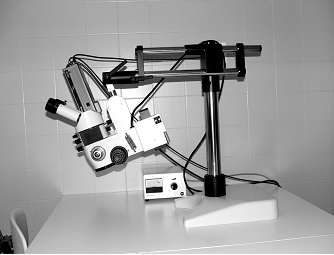
The Leica Wild M650 microscope
Instrumentation
Operative
microscopes
Microscope maintenance
Basic
microsurgical instruments
Non-microsurgical instruments
Protection and maintenance
Magnetization
Coagulation, bipolar coagulator
Microsurgical threads
Other requirements
[ back to top ]
Operative microscopes
The microscope is supplied by an adjustable stage and it is for individual use. In the clinical practice, the height and focus of the microscope are adjustable by feet, but manually adjustable zoom and focus are equally acceptable for educational use. Beam splitters which provide opportunity for the assistant to see the same operative field and which serves also documentation purposes also represent important accessories in the clinical use. The most suitable microscopes are Zeiss and Leica (Wild) products which have excellent optical system. Apart from this, the quality of the light source is also important. This is aided usually by a light halogen source supplied by a flexible fiber optics connected to the microscope or bringing light directly to the operative field. It is also adjustable, therefore everyone can work with an individual light intensity. The ideal focus distance of the optical lenses should be 200 mm, the maximal enlargement of the objective should be 12.5x. With such a microscope we are able to achieve 4-20 times enlargement, which is really satisfactory. We start the use of the microscope with switching the light source and adjusting light intensity. Then we check the adjustable functions such as focus and zoom, and inter-pupillary distance and correct dioptry.

The Leica
Wild M650 microscope
[ back to top ]
Microscope maintenance
Every time we use the microscope, the objective and eyepiece lenses should be cleaned, but only with a suitable material to avoid scratching the glass surfaces. We try to protect the microscope from dust, therefore always cover it with a protecting bag after finishing the work. When moving the microscope, be careful not to cause any damage to it. Preferably move the headpiece and the stage separately if the microscope needs to be relocated.
[ back to top ]
Basic microsurgical instruments
Instruments used in microsurgery are simple, but should be of excellent quality. The movements performed during microsurgical procedures are the finest in the whole surgery, therefore the use of in-suitable or injured instruments causes frustration and jeopardize the improvement of microsurgical skills.
a. Forceps
The iris forcep is used during the preliminary manual exercises to stitch the
strings of a gauze net, however it can also be used in the in vivo
experiments to grab soft tissues. The surface of the tip is serrated, similarly
to the surgical - so called - “anatomical” forceps.
The straight, fine-tipped jeweler forceps (Adson) are used to
grab or lift the tissue and tie thread. In closed position, the grab-surface
should be at least 3 mm, this makes the grip secure. The vessel dilator is
virtually a modified jeweler forceps, the grab-surface is smooth and the tip is
rounded. By entering it into the vessel it can be easily opened up, but we also
use it to counter-hold when making a suture.
 |
Different
types of microsurgical forceps: a: jeweler (Adson) forceps, b: anatomic (short-handled) forceps, c: long-handled forceps, d: curved-tipped forceps, e: slightly curved-tipped forceps, f: straight invert forceps, g: curved-tipped invert forceps. On the right a match stick shows the size. |
b. Needle holders
The needle holders are used to grab the needle and have various size and shape (supplied with flat or cylindrical handle and with or without closure structure). Mostly needle holders without closure structure are used in microsurgery.
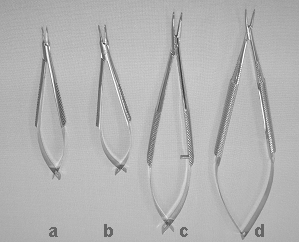 |
Different
types of microsurgical needle holders: |
c. Scissors
The dissecting scissors are characterized by a springy handle, a slightly curved blade and a rounded tip. This latter characteristic is necessary to avoid damaging the vessel wall during preparation. Adventitia scissors are used for removing the adventitia layer from the ending of a vessel, it is characterized by a straight blade and a fine, spiked tip. It is also suitable for cutting the thread, as it does not fracture it.
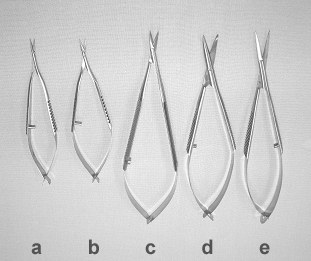 |
Different
types of microsurgical scissors: a: small sized, straight adventitia scissors with tapering blades b: small sized, straight adventitia scissors with curved tapering blades, c: long scissors with short, curved tapering blades d: long scissors with long, straight blunt blades e: long scissors with long, straight tapering blades. |
d. Vessel clips
Vessel clips are applied for fixing the vessels, and positioning the cut endings in the proper position. They press the vessel without causing any trauma.
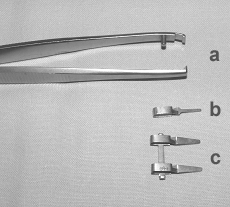 |
a:
microsurgical clip applicator, b: clip, c: approximator |
[ back to top ]
Non-microsurgical instruments
Scalpels are used to perform incisions, a fine anatomic forceps and fine scissors are also applicable. Since these precision instruments are very fine, sensitive and expensive, a special instrument case is mandatory to protect them. It is useful if it is sterilizable, and if each instrument has a separate box.
[ back to top ]
Protection and maintenance
If we want
to use our tools for a longer period of time, we have to handle them with
special care. Pay attention to the followings:
· Their tip must not hit by a solid surface.
· You
must not put down the instruments with their tip downwards.
· Always
put them onto a safe place, from where they can not fall down.
· It
is important to keep only one instrument in your hand at a time.
It is advisable to soak the instruments in a hemolytic bath for 30 minutes,
after which even the most persistent contamination can be easily washed off.
After drying, the instruments shall be stored carefully. Even minor maintenance
works (sharpening, oiling, grinding, etc.) should be done by a specialist.
Organizing microsurgical instruments can enhance productivity, simplify the
process of replacing missing or damaged instruments, and help to maintain
complete instrument sets in service. Most institutions utilize hard
sterilization metal containers for the instrument sets. Containers should have
identification tags both outside the container and on the inner basket. In the
containers delicate instruments should be segregated from larger, heavier
patterns. To avoid dulling scalpel and scissor blades, a sterile cloth could be
put into the container. Many containers offer dividers, pins and silicone mats
that can be utilized to organize the instrument tray into instrument handling
systems. By dividing the tray into compartments and using or cradles for
delicate instruments, damage caused by the random placement of instruments can
be avoided.
 |
 |
[ back to top ]
Magnetization
It may happen sometimes, that the instrument becomes magnetized, if it touches a device that has some magnetic or electromagnetic parts. In these cases it is advisable to purchase special equipment that is able to remove magnetism. Without this intervention, grabbing of the needle or even the thread becomes difficult.
[ back to top ]
Coagulation, bipolar coagulator
To handle bleeding in microsurgery, a special modified version of bipolar coagulator is used. In monopolar coagulation, electricity is spread in the tissues from the active electrode to the neutral one while at bipolar coagulation, the electricity passes only the tissues held between the tips of the forceps.
Rules
a. Since the electric current passes only between
the tips of the bipolar forceps during bipolar coagulation, the thermal effect
that produces the coagulation can be very well controlled.
b. A common problem
we are facing is the adhesion of your forceps to the tissues. This can be
prevented by the following means:
· use
the coagulator at the lowest level that produces a visible effect.
· keep
the tissues and the tips of the bipolar forceps always moistened.
· Do
not squeeze the vessel walls between the tips of the forceps. Instead, gently
touch and slide the tip of the forceps back and forth obtaining a considerable
coagulated surface.
· Often
clean the tips of the forceps and moisten them with gauze swabs.
· During
coagulation of a vessel branch, pull the main vessel apart with the forceps in
the opposite direction of the branch, in order to protect it from the emitted
heat.
[ back to top ]
Microsurgical threads
We use cylindrical microsurgical needles with 7/0, 8/0, 9/0, 10/0 monofil thread. The needle can be 100 and 75 μm in diameter, the previous is used in basic practicals, the latter is for more complicated operations.
[ back to top ]
Other requirements
a.
Furniture
The working table is optimally 80 cm high.
Stability is an important factor, and there should be enough places for the
knees and legs under it. If two students are sharing a table, the surface should
be 53-57 cm wide. Adjustable height and convenience are the basic requirements
for a chair, back-rest is not really necessary.
b.
Surgical glove sheet
To learn the first steps of sutures we use an
incision on a sheet of surgical glove. To fix the piece of surgical glove, an
8x8 cm square shape cardboard paper should be cut, and a 2 cm side-length square
window should incised in the middle. We should mount a 3x3 cm rubber piece on it
and fix with a tape by stretching the glove until the wrinkles disappear.
Overstretching makes the rejoining of the edges of the cut also difficult.
During the work, this paper frame should be mounted firmly to the working pad.
c.
Background
The colour of the material placed in the
background of our working area has to be in contrast with the colour of the
vessel. Dark green or dark blue colours are advisable.
d. Other
surgical requirements
To keep the vessel wet, a 20-ml syringe with a
needle and Ringer’s lactate solution has to available. Gauze pads are also
required to soak up the fluid from the area of the operation.